Now the Internet industry is growing day by day, people's demand for the Internet is increasing, and the requirements for network speed and bandwidth are also getting higher and higher. Comparing the previous network speed with the current network speed, we can find that the speed of the network speed has almost doubled. What about the one that transmits the signal? Let's take a look
Optical Fiber Communication
The principle of optical fiber communication is actually not complicated. It is to first turn the transmitted information (such as voice) into an electrical signal at the sending end, and then modulate it to the laser beam emitted by the laser, so that the intensity of the light varies with the amplitude (frequency) of the electrical signal. At the receiving end, the detector converts the optical signal into an electrical signal after receiving it, and restores the original information after demodulation.
Optical communication is that the light-emitting diode LED or the injection laser diode ILD sends out the light signal and propagates along the optical medium, and at the other end, there is a PIN or APD photodiode as a detector to receive the signal. The modulation of the optical carrier is the amplitude shift keying method, also known as the brightness modulation (IntensityModulaTIon). A typical approach is to represent two binary numbers with the appearance and disappearance of light at a given frequency. Both the light-emitting diode LED and the injection laser diode ILD signal can be modulated in this way, and the PIN and ILD detectors respond directly to the luminance modulation.
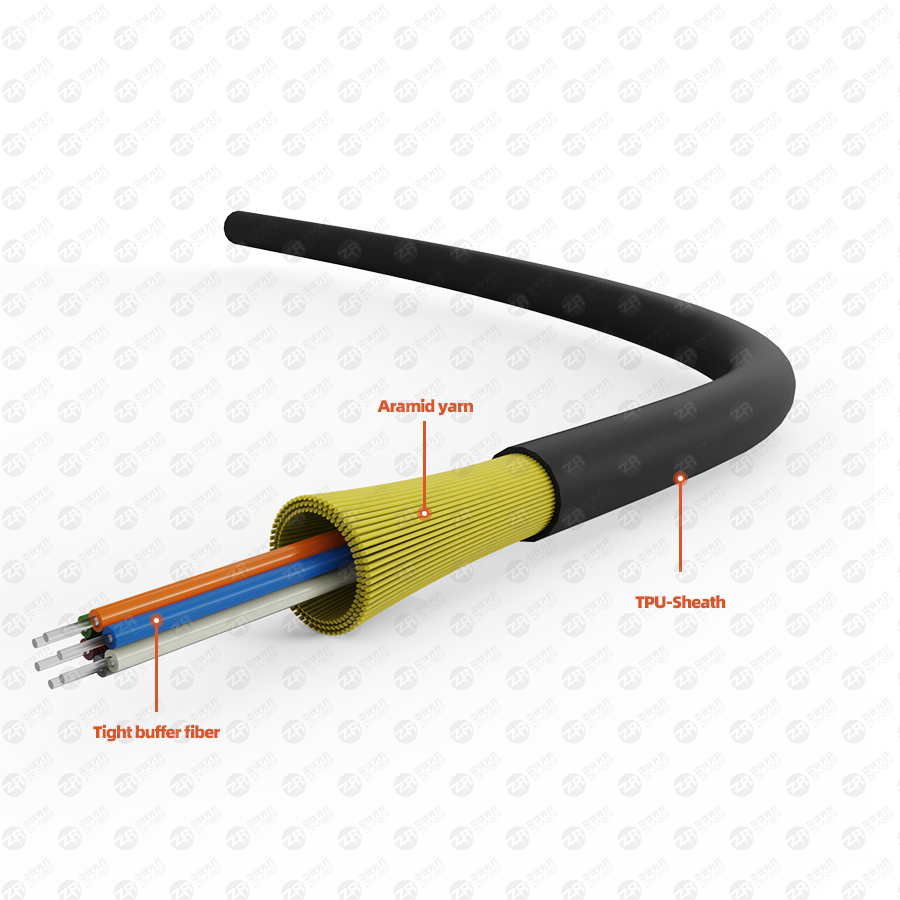
Optical fiber communication is a communication method that uses light waves to transmit information in optical fibers. Due to the significant advantages of lasers such as high directivity, high coherence, and high monochromaticity, the light wave in optical fiber communication is mainly laser, so it is also called laser-fiber communication.
Power amplification: The optical amplifier is placed before the optical transmitting end to increase the optical power of the incoming fiber. The optical power of the entire line system is improved. Online relay amplification: when the building group is large or the distance between buildings is long, it can play the role of relay amplification and improve the optical power. Pre-amplification: Amplify the micro-signal after the photodetector at the receiving end to improve the receiving capacity.
Optical cables are not easy to branch, because they transmit optical signals, so they are generally used for point-to-point connections. Experimental multipoint systems with optical bus topologies have been built, but are still too expensive. In principle, due to the small power loss and attenuation of optical fiber, there is a greater potential for bandwidth. Therefore, the number of connectors that can be supported by general optical fiber is much more than that of twisted pair or coaxial cable. The low-cost and reliable transmitter is a 0.85um wavelength light-emitting diode LED, which can support a transmission rate of 100Mbps and a local area network within the range of 1.5 to 2KM. Laser diode transmitters are expensive and cannot meet the million-hour lifetime requirement. The LED detector PIN operating at 0.85um wavelength is also a low-cost receiver.
The application of optical fiber is also very extensive, ranging from the link of enterprise servers to the Internet access of households. Now the network has entered thousands of households and can be said to be integrated into our life. A faster and more convenient 5G network is worth looking forward to.