When natural disasters or external buildings and other obvious external forces cause the optical cable line to be blocked, the inspector will carefully check the optical fiber cable route according to the fault phenomenon and the approximate fault location provided by the tester, and it is usually easier to find the fault location. If this were not the case, inspectors would have difficulty finding fault locations from anomalies along the route. So, how to improve the accuracy of optical cable fault location?
Indoor and outdoor leather cable
(1) Correct use and instrumentation
Accurately set the parameters of the OTDR, select the appropriate test range file, apply the zoom function of the instrument, and place the swimming standard at the corresponding inflection point, such as the fault point, the inflection point. Test results.
(2) Create accurate and complete source data
Accurate and complete optical cable data is the basic basis for determining obstacle measurements. Therefore, attention must be paid to the acquisition of line data. , organize and review work, and build true, trusted and complete line data.
(3) Establish accurate line routing information
Includes standard stone (number of poles) - fiber length (cable length) comparison tables, "Fiber Length Cumulative" and "Fiber Attenuation" records. When establishing Fiber Length Accumulation data, both ends should be measured from both ends. The distance from the station to each connector, in order to test the results accurately, the transition fiber can be used according to the situation. Various inspection lengths are collected and recorded by inspection and acceptance personnel. The more careful the registration, the smaller the error in obstacle determination.
(4) Establish complete and accurate line data
The establishment of line data not only includes a large amount of data in the line structure, completed technical documents, drawings, test records and pictures of the backscattered signal curve of the relay part of the fiber. (For example, the twist rate of the fiber, the refractive index of the fiber, etc.), these data are the basis and comparison basis for future obstacle testing.
(5) Perform the correct conversion
In order to accurately determine the location of the fault point, the length of the fiber optic cable under test must also be converted to the ground length from the test end (or connector point) to the fault point.
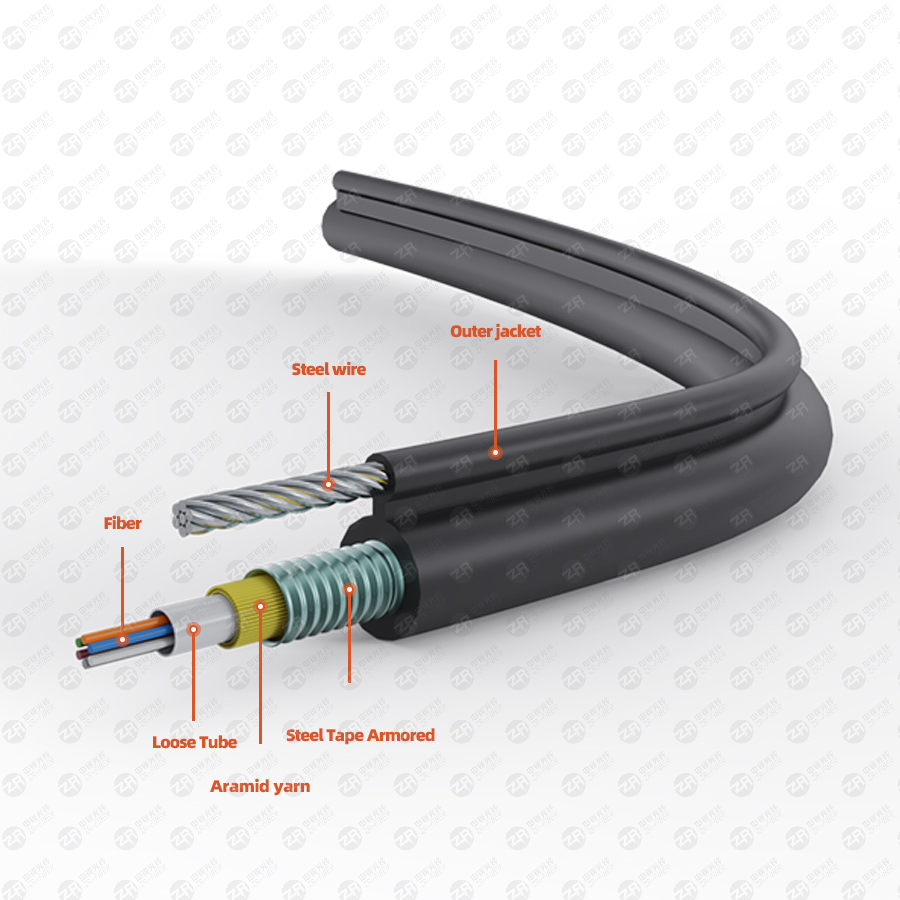
Analysis of the cross-section of indoor and outdoor optical fiber cables
The grounding length from the test terminal to the fault point can be calculated by the following formula (the unit of length is m):
L=[(L1-L2)/(1+P)-L3]/(1+a) In the formula, L is the ground length (in meters) from the test end to the fault point, and L1 is the distance from the test end by the OTDR The fiber length (in meters) to the point of failure, L2 is the remaining fiber length in the disk of each connector enclosure. (in meters), L3 is the cable, all reel lengths (in meters) on each connector, and P is the shrinkage (ie, twist factor) of the fiber in the cable. It is best to use the value provided by the manufacturer. Usually 7‰, a is the natural bending rate of the optical cable (0.5% for pipeline laying or overhead laying, 0.7%-1% for direct buried laying). With accurate, complete source data, the length of the failed fiber measured by the OTDR can be compared to the source data to pinpoint the location of the point of failure.
(6) Maintain the consistency of the obstacle test and test conditions to the data
During fault testing, try to keep the test instrument's signal, operating method, and instrument's parameter settings consistent. Because optical instruments are very precise, if there is a difference, it will directly affect the accuracy of the test, resulting in the difference between the two tests themselves, making the test results unparalleled.
(7) Flexible testing and comprehensive analysis
Typically, bidirectional fault testing can be performed at both ends of the fiber optic line, and the location of the fault point can be calculated by combining the raw data. The test and calculation results in two directions are comprehensively analyzed, and compared with , to make the judgment of the specific location of the fault point more accurate. If there are no obvious features on the route near the obstacle point and a specific obstacle point cannot be identified on site, methods such as measuring at the nearest seam or excavating at the obstacle point for preliminary testing can also be used. Look for curve changes at any time to find the exact point of fiber failure.
The above is how to improve the accuracy of fiber optic cable fault location. Of course, we can check the raw data by measuring the distance from the fault point to the test end through the OTDR to find out which two marks (or which two joints) need to be converted, and then find the specific location of the fault point. Bidirectional testing can be performed if conditions permit, which is more helpful in pinpointing the specific location of the point of failure.
https://www.ductcable.com/product?productId=908d6b970bcc46aa97fb1db876894ac5